The pain in the neck is an alarming sign.Perhaps this is just an overvoltage and you just have to relax and relax.But what if the pain is associated with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?It is important to carefully consider symptoms and treatment, because complications can affect the most important organ - the brain.
What is cervical osteochondrosis
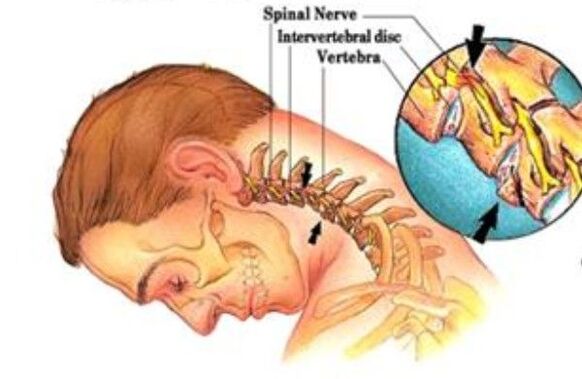
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a degenerative disease of the bone-cherry system of the body.It leads to the destruction of the cervical intervertebral discs, the growth of bone tissue of the vertebrae, the formation of growths on their surfaces.
The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae, the first of which is articulated with the skull.The anatomical and functional unit of the spine is the spinal-motor segment.This is a joint complex, due to which the spinal column moves.The complex consists of two vertebrae, the intervertebral disc, the articular surfaces of the vertebrae (facet), nerves, ligaments and muscles.
Osteochondrosis begins with damage to the intervertebral disc and affects all surrounding tissues.Over time, the process leads to a violation of the biomechanics of the spine as a whole.With the development of osteochondrosis, hernias of intervertebral discs, squeezing nerve roots and blood vessels can form.
Pathological processes in the intervertebral disk take place four stages: diet, weakening of the ligaments, damage to the disk and compression of the nerves.
- Stage 1.The conditions of the power and metabolism of the intervertebral disc are violated.Due to the features of the structure, discs are eaten only during movement.If it is not, dystrophic tissue changes begin: the disk is starving and dehydrated.Loss of water leads to the fact that the intervertebral disc cannot perform the functions of depreciation.The load on the fibrous ring intensifies, cracks and tears appear in it.At this moment, minor pain may appear.
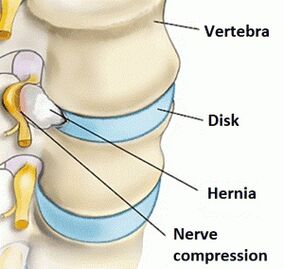
- Stage 2.At the second stage, the ligamentous apparatus of the vertebral segment occurs.The connection becomes pathologically mobile.The pathological process in the disk is aggravated, the hernia (prolapse) begins - seeping the pulpoose nucleus through cracks in the fibrous ring.The pain becomes periodic.
- Stage 3.Further, the intervertebral disc is completely damaged.The pulpoose core of the disk goes beyond the fibrous ring.The resulting hernia can infringe on the nerve roots.The inflammatory process develops.This is manifested by an exacerbation of pain, the so -called radicular syndrome.
- Stage 4.At the fourth stage, the defeat affects nearby fabrics.It is possible to squeeze the radicular artery, which leads to the lack of blood supply to the spinal cord.As a result, the spine can be completely immobilized.
The first signs and main symptoms
At the beginning of the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical region, discomfort, limitation of movement, soreness of the neck.Often this does not attach importance.
Over time, the pain intensifies, become aching, burning, head, neck, shoulder blades, shoulders hurt - perhaps this develops the syndrome of the vertebral artery.The artery is squeezed or spasmodic, blood flow is disturbed.
At 1-2 stages of cervical osteochondrosis, ophthalmological problems associated with spasm in the vessels often occur.Darkening in the eyes, flickering, the appearance of “flies”, colored spots in front of the eyes - all these are symptoms of osteochondrosis.
The most frequent symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Migraines, dizziness, nausea and cough.
- Hearing impairment, pain in the ear, face.
- Motor disorders in the hands, legs.The sensitivity of the skin on the head may be a gap.
- Pain in the hand.If a nervous spine is pinched, then the entire area in which he sends impulses can hurt or “fall out”.
In addition to the above symptoms, you can distinguish three main pain syndrome, accompanying osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.The syndrome is a whole complex of symptoms.The determination of the leading pain syndrome is important, since the entire treatment regimen is built precisely on eliminating pain.And it is impossible to eliminate it without knowing origin.
- Miofascial syndrome- pain in skeletal muscles and adjacent fascia.The violation is associated with overload, in which spasm, hypertonicity, painful nodes inside the muscles (trigger points) occur.
- Rook syndrome- The pain caused by prolonged squeezing of the roots of the spinal nerves.The process of hernial formation for osteochondrosis of the spine leads to a pinching of the nerve fibers and the subsequent inflammatory reaction.The pain spreads along the nerve.
- Facet syndrome- pain in the vertebrates.The vertebrae from the second cervical have articular processes, which are interconnected by arched (facet) joints.With osteochondrosis, intervertebral discs are destroyed, their height decreases, and this leads to the fact that the joint capsules of the arched joints are in constant tension.This causes pain.Moreover, the pain increases by the end of the day, especially with a long -term forced position.
The causes of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine One of the key causes of osteochondrosis is the evolution of the spine to a high vertical load.The ancestors of people walked on four legs, like other mammals.They did not suffer from osteochondrosis, since in the horizontal position of the body intra -disconed pressure is half as much as in vertical.By the standards of evolution, the transition to straightening occurred not so long ago, and the spine simply did not have time to adapt to a high vertical load.So, along with the straightening, a person also acquired diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
An even more vulnerable neck of a person makes its structure.The cervical department of a person consists of seven small mobile vertebrae, which are articulated by the type of children's pyramid.This design can hardly be called stable outside the rest of the rest.In addition, the muscle frame in this zone is weak, and the loads can be high - all this makes the neck vulnerable.Any injury is fraught with consequences.Even if the damage was in another spine, the load redistribution can cause osteochondrosis.
Another factor is aging.The formation of the skeleton and cartilage fabric ends by 21 and after that the irreversible process of aging (degeneration) begins.Foods of cartilage is carried out only due to diffusion, and if the intervertebral disk does not receive nutrients, it begins to gradually collapse.
In addition, the development of cervical osteochondrosis contributes to:
- Autoimmune diseases.They involve their own body cells in the pathological process of the destruction of the cartilage tissue.
- Infections, hormonal failure, deceleration in metabolism - all these circulatory disorders can also serve as factors for the development of osteochondrosis.
- A sedentary lifestyle, working conditions under which a person spends most of the time in a forced static position.
- High loads leading to injuries can lead to compression.
- Genetic defects associated with the weakness of the musculoskeletal system and the inferiority of the cartilage fabric.
The spinal canal in the cervical spine is very narrow, so high loads, any violation or injury can lead to compression of the spinal cord.And this is very dangerous.
In addition, a large number of nerve endings and blood vessels pass in this area.If the blood stops flowing into the brain in the proper volume, a stroke may happen.
Diagnostics
In the primary diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, the doctor collects the patient’s history.He finds out that and how it hurts, with what intensity, with a load or at rest, at what time of day it hurts stronger, whether the cervical spine has occurred.
During the examination of the neck, the doctor feels the cervical vertebrae and muscles, lymph nodes;Assesses the volume of movements, excludes or confirms the rooser syndrome.
After that, a laboratory diagnosis is prescribed to exclude autoimmune diseases: a general blood test, ESR, rheumatoid factor, antigen HLA B27.
The main role in the diagnosis is given to radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
- RntgenographyIt helps to evaluate the condition of bone structures, soft tissues and cartilage in the pictures are not displayed.To visualize these structures, contrast medium is introduced: angiography, discography, myelography.
- Computed tomography (CT).This method also uses the principle of radiography, but using computer processing, you can get a series of pictures of longitudinal and transverse sections on which you can see bone and cartilage.
- Magnetic resonance tomography (MRI).It is a “gold standard” in the diagnosis of pathologies, including cartilage and soft tissues.MRI gives an idea not only about the structure of organs and tissues, but also their functioning.In the case of osteochondrosis with a frequent complication, there is a hernia of the spine.MRI allows you to diagnose the process of hernia formation in the early stages.
Treatment
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is reduced to conservative methods.Initially, the pain syndrome is removed, and then various procedures are prescribed.But in the most extreme cases, when the pain does not pass for more than three months and medicines do not help, surgery becomes the only way out.
Non -surgical treatment methods
Osteochondrosis has struck the bone -ocal system for more than one year, and therefore treatment will take time.Patience must be gained.Conservative treatment tasks:
- Eliminate pain.
- Remove inflammation.
- Restore the functions of spinal roots.
- Strengthen the muscle corset and ligaments.
Conservative treatment includes drug therapy and physiotherapy.Preparations help relieve pain during the exacerbation, and physiotherapy - to launch the processes of self -healing the body.
During severe pain with radicular syndrome, the so -called “blockade” is performed: the drug is administered in the immediate vicinity of the inflamed spine of the spinal nerve.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is based on natural and artificially recreated physical factors: cold, heat, electric current, magnetic radiation, laser and others.For their reconstruction, special devices, devices, manual methods are used.
- Laser therapy- Biological activation of the processes of regeneration of the intervertebral discs.The body begins to self -heal.
- Plasmotherapy (PRP therapy)- injections of plasma isolated from the patient's blood.Plasma is rich in platelets, growth factors, hormones.After injection, local immunity rises, regeneration processes are launched.
- Acupuncture- Stimulation of nerve endings with special needles.Improves metabolism in affected areas, relieves pain.
- Shock wave therapy- exposure to high -frequency waves.Allows you to start natural recovery processes.
- Kinesitherapy- Movement therapy.It can be active (exercise therapy) and passive (massage, traction).LFK strengthens the back muscles, traction relieves tension and pain.It is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Manual therapy and massage- exposure to soft tissues and joints in order to restore equilibrium in the body and synchronization of processes.Return mobility and eliminate pain.
- Taping- gluing special plasters on the skin in places where it is necessary to affect the receptors of stretching and compression of the muscles.It can both relax and increase the tone.
In the period of acute pain, the patient is recommended to wear special bandages and collars to the neck.
The positive effect of conservative treatment is achieved in 2-3 months. If there is no result, the patient is recommended.
Surgical methods of treatment of osteochondrosis
Operation in the case of cervical osteochondrosis is an extreme measure for which special indications are needed.The operation is recommended if:
- The pain cannot be removed by therapeutic treatment for more than 3 months.
- There is a hernia of the intervertebral disc.
- Sensitivity in the limb disappears
Postoperative rehabilitation also takes time and may include therapeutic treatment.
Cervical osteochondrosis is a complex degenerative disease.You can’t treat it.Such serious violations in the musculoskeletal system can lead to disability.The pain in the neck can become chronic, osteochondrosis will spread to several parts of the spine.Timely prevention can prevent the development of this disease.
Prevention
To maintain the health of the cervical spine, daily physical activity is necessary.The food of the intervertebral discs occurs in motion, so it is extremely necessary.It is important that the loads are optimal and regular.
If the work is related to constant finding in a static position, a periodic warm -up is needed.And at home after a working day you can lie on your back on a flat surface for some time, putting a roller under the neck.This method will help restore the cervical bend of the spine, remove muscle tension.
In the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis, the correct pose during sleep is important.If a person in the morning rises with pain in his neck, then the muscles did not have time to relax and recover.
Here, an orthopedic pillow, which is selected individually, for 3-5 years will help.
Do not postpone treatment
A doctor will help you choose a recovery program.He will evaluate the condition of the spine on MRI images, report the probability of resorption and the possibility of treatment.























